All About the Elbow

Did you know . . .
- the elbow is one of the most active parts of the body, used for virtually any activity that involves your hands,
- elbows can be a very destructive body weapon that anyone can put to use in a matter of seconds,
- elbowing is illegal in soccer. If you’re caught elbowing your opponent during the soccer pitch, it’s not only frowned upon but it will result in the opposing team getting a free kick.


The elbow is not a simple joint. Your elbow allows you to lift, swing, throw and hug, for starters.
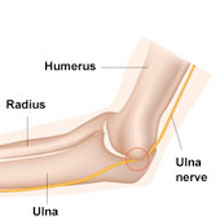
The elbow’s a joint formed where three bones come together – the humerus, your upper arm bone and the ulna and radius, the two bones that make up your forearm. Each bone has cartilage on the end that helps them slide against one another and absorb shock. They’re lashed into place with ligaments (tough tissue). The tendons connect the bones to muscles that allow you to move your arm in many different ways. If something happens to any of these parts or the blood vessels and nerves around them, it can cause pain.
Elbow injuries can be minor or serious and may include the following symptoms:
- swelling
- pain
- weakness
- tingling
- numbness
- decreased range of motion
INJURIES
As we mentioned, your elbow is not a simple joint. Unfortunately, they’re several ways you can injure your elbow:
Sudden (Acute) Injuries:
Some injuries are one-time injuries, hopefully, like when you fall or get hit hard while engaging in sports. These injuries include:
- dislocated elbow: when one of the bones that forms the elbow gets knocked out of place
- fractured elbow: if one of your arm bones breaks at the elbow, you have a fracture. Commonly, this occurs with a sudden blow, as you might get while playing a contact sport or in an auto accident.
- strains and sprains: when muscles get stretched or torn, you have a strain. When it’s ligaments that are torn or stretched, you have a sprain. A strain may occur when you put too much pressure on your elbow muscles, i.e. when lifting a heavy object or overdoing it with sports. An elbow sprain is often found in athletes who throw, use racquets or play contact sports.
Overuse Injuries:
Other injuries are considered wear-and-tear injuries and occur over time, as you repeat certain motions or actions and put wear-and-tear on your elbow. These injuries can occur while playing sports or in any number of work settings, from a factory to an office.
- bursitis: commonly caused by repeating the same motion over and over, you can also get bursitis from an infection or accident. Bursa are small sacs with fluid in them. You have bursa in your joints to help cushion your tendons, muscles and bones. Bursa also helps skin slide over bone. However, when they get swollen, they can cause pain.
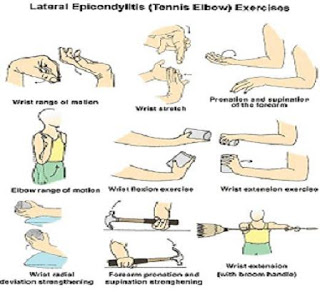
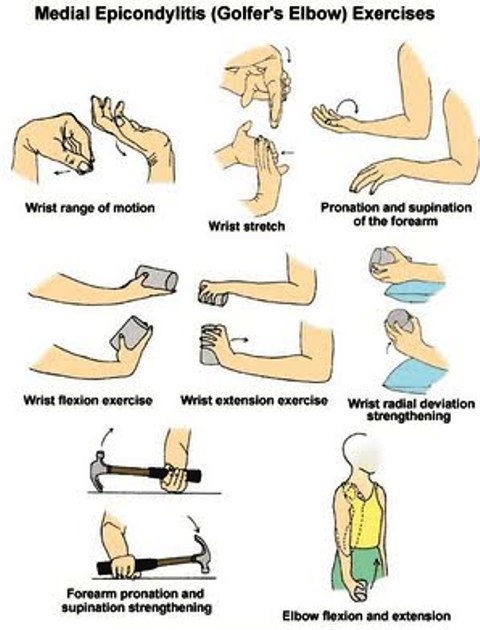
- tennis elbow and golfer’s elbow: both are types of tendinitis, meaning you have swelling in the tendons around your elbow from overuse. Despite the names, the injuries aren’t limited to tennis players or golfers. The main difference between the two is that golfer’s elbow affects the inside of your elbow, tennis elbow affects the outside.
- stress fractures: a small crack in one of your arm bones, commonly from overuse. The pain is usually worse when throwing.
- trapped nerves:
- cubital tunnel syndrome: one of the main nerves in your arm (the ulnar nerve) gets squeezed as it runs along the inside of your elbow and passes through tissue (cubital tunnel). This may cause numbness or burning in your fingers, hand and arm.
- radial tunnel syndrome: a similar issue with the radial nerve as it passes through the radial tunnel near the outside of your elbow. This can cause numbness or burning on your outside forearm and elbow.
Diseases:
Several diseases may also cause elbow pain, however, it’s usually not the main symptom:
- arthritis: several types of arthritis can affect your elbow, rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis are the main:
- rheumatoid arthritis: the most common type of arthritis in the elbow. Your immune system attacks your body’s healthy tissue and causes swelling in your joints.
- osteoarthritis: when your elbow cartilage breaks down over time, meaning the bones rub together and cause stiffness and pain.
- osteochondritis dissecans: most common in children and teens, a piece of bone near the elbow dies. The bone piece and some cartilage then break off, causing pain during physical activity.
- lupus: your immune system attacks healthy parts of your body, including your organs and joints.
- lyme disease: carried by ticks, it can cause severe problems if not treated early. Typical problems occur in your nervous system and cause pain in your joints, such as your elbow.
- gout: a type of arthritis. When uric acid, normally a waste product is sent out of your body and builds up as crystals in your tissues. If the buildup happens in your elbow, it may be very painful.

TREATMENT
Treatment varies based on your elbow injury and the symptoms you’re experiencing. Treatment options include:
- rest
- ice
- physical therapy
- braces/elbow padding
- injections
PREVENTION
Again, most elbow disorders are the result of injury or overuse. Do the following to prevent elbow disorders or injury:
- warm up and stretch properly
- use the proper grip on sports equipment
- correct improper sports techniques or mechanics
- use proper tension on racquets or sports equipment
- use elbow padding
- take breaks from repetitive tasks
- practice exercises that help to strengthen the muscles around your elbow joint
To learn more about the elbow, tune into Inside Sports Medicine this Sunday, June 3rd at 8 am EST on 97.1 The Ticket and watch us on Facebook Live.
ABOUT MICHIGAN SPORTS & SPINE CENTER:
We’re innovative leaders utilizing cutting-edge technologies such as musculoskeletal ultrasounds, PRP, stem cell treatment, and other innovative procedures. Michigan Sports & Spine Center is committed to resolving your pain, not simply masking it. We treat the whole body, not just the injury, and perform preventative treatment so your injury doesn’t come back. Our studies prove that Michigan Sports & Spine Center has patient success rates much higher than the national average. We treat everyone from high-profile athletes to your neighbor next door. Our primary focus is getting our patients back into the game of life!
Sources: WebMD, University of Michigan Health, Healthline
