Low Back Pain, A Universal Human Experience?
Did you know . . .
- 31 million Americans experience low-back pain at any given time,
- each year, half of working Americans admit to having back pain symptoms,
- most cases of low back pain are mechanical or non-organic, meaning they aren’t caused by serious conditions (infection, fracture, inflammatory arthritis or cancer).

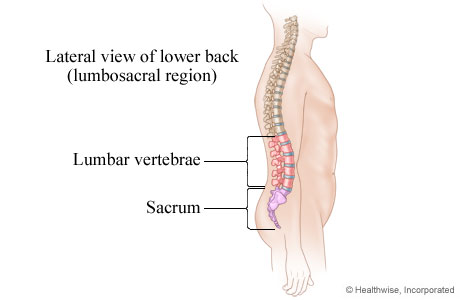
Low back pain is a universal human experience, nearly everyone will experience low back pain at some point in his or her life.
The lower back starts just below the ribcage and is called the lumbar region. The pain felt here can be intense and is a leading cause of disability worldwide. Low back pain is one of the top causes of missed work and one of the most common reasons people visit the doctor.

CAUSES
Symptoms of low back pain can range from a dull ache to a shooting or piercing sensation. The agony can make it hard to stand up straight or move.
Low back pain that comes on suddenly and lasts less than six weeks is known as acute pain and may be the result of lifting something heavy or by a fall. Pain that lasts more than three months is known as chronic pain and is less common than acute pain.
Causes frequently linked to back pain:
- arthritis
- osteoporosis
- muscle or ligament strain
- ruptured or bulging disks
- skeletal irregularities
- herniated disc
Unfortunately, anyone (children and teens included) can develop low back pain. There are several risk factors that can contribute to low back pain:
- lack of exercise: frail, unused muscles
- age: around the 30 – 40 year age range, back pain becomes more prevalent
- excess pounds: carrying extra weight puts extra stress on the back
- improper lifting: using your back instead of your legs can cause pain
- poor posture
- smoking: can keep the body from distributing nutrients to the discs in our backs
- diseases and sicknesses: some types of cancers, arthritis, blood clots, kidney infections, kidney stones and bone loss can contribute to back pain
- psychological conditions: people prone to anxiety and depression have an increased risk of lower back pain
Sports injuries and vehicle accidents can cause low back pain, commonly the simplest of movements (bending over or moving incorrectly) can have terribly painful results.
TREATMENT
Fortunately, low back pain often gets better on its own, however, you should see Michigan Sports & Spine Center or another specialist if you’re experiencing low back pain.
There are several effective treatment options for low back pain:
injections:
- trigger point injections: a procedure used to treat painful areas of the muscle that contain trigger points, or knots of muscle that develop when muscles do not relax, involves the injection of medication directly into the trigger point
- epidural injections: an injection into the spine, delivering steroids that can provide low back pain relief by reducing inflammation
manipulations:
- by applying pressure to the bones and the surrounding tissues the treatment reduces pain, commonly decreasing the need for meds
- rapidly advances physical therapy
- requires very few passive forms of treatment, such as bed rest
physical therapy/exercise training:
- the combination of exercise training and physical therapy usually includes stretching, strengthening and low-impact aerobic exercises
massage therapy:
- improves blood flow and reduces muscle stiffness
acupuncture:
- an ancient Chinese medical practice that seeks to ease the pain by balancing the body’s natural energy pathways and releasing serotonin, a ‘feel-good’ chemical that relieves pain and discomfort
EASE BACK PAIN
There are several things that we can do to avoid lower back pain or prevent the pain from coming back. We can improve our physical condition and learn and practice proper body mechanics.
Keep your back healthy and strong:
- exercise: low-impact aerobic activities can increase endurance and strength in your lower back and allow your muscles to function better.
- walk: studies suggest that a simple regimen of daily walking can help individuals with lower back pain. It’s literally as simple as taking a stroll through the park! When people walk actively, abdominal and back muscles work in much the same way as when they complete exercises that target these areas.
- stretch
- practice yoga: there’s various study’s and evidence that proves yoga works
- maintain a healthy weight: if your overweight, slimming down can prevent pain
- use proper body mechanics: stand smart, maintain a neutral pelvic position. Sit smart, choose a chair with good lower back support, a swivel base and armrests. Lift smart, and avoid heavy lifting.
Tune into Inside Sports Medicine this Sunday, January 28 at 8 am EST on 97.1 The Ticket and hear us talk about low back pain.

ABOUT MICHIGAN SPORTS & SPINE CENTER:
We’re innovative leaders utilizing cutting-edge technologies such as musculoskeletal ultrasounds, PRP, stem cell treatment, and other innovative procedures. Michigan Sports & Spine Center is committed to resolving your pain, not simply masking it. We treat the whole body, not just the injury, and perform preventative treatment so your injury doesn’t come back. Our studies prove that Michigan Sports & Spine Center has patient success rates much higher than the national average. We treat everyone from high-profile athletes to your neighbor next door. Our primary focus is getting our patients back into the game of life!
Sources: American Chiropractic Association, National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, WebMD, Mayo Clinic
